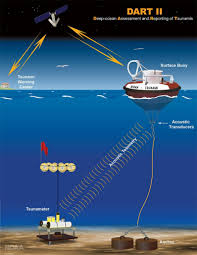
Development of an operational tsunameter was an extraordinary engineering accomplishment. The task was to design, develop, test, and deploy real-time reporting, deep ocean instrumentation capable of surviving a hostile ocean environment while performing with the quality and reliability demanded of an operational tsunami warning system. To measure tsunamis many technologies has been tested.
At present the best way known to detect a tsunami is to measure very accurately water pressure on the sea bottom. The tsunami detection algorithm works by first estimating the amplitudes of the pressure fluctuations within the tsunami frequency band and test these amplitudes against a threshold value. The pressure acquisition station is a critical component of the tsunameter system and includes an ultra stable, high precision, high accuracy, pressure depth sensor, a computer, a data logger and an acoustic modem to communicate with surface buoy. The remarkable performance of depth sensor is achieved through the use of a precision quartz crystal resonator whose frequency of oscillation varies with pressure-induced stress. A quartz crystal temperature signal is provided to thermally compensate the calculated pressure and achieve high accuracy over a broad range of temperatures. The depth sensors include waterproof housings with integral shock protection buoy. The bottom pressure recorder (BPR) is a critical component of the tsunameter system and includes a Digiquartz Broadband Depth Sensor, a computer, data logger and an acoustic transducer to communicate with the surface buoy
Tsunameter BPR The Digiquartz Broadband Depth Sensor is the main sensing element in the bottom pressure recorder. This sensor monitors pressure continuously and if the pressure reading changes above a set threshold, then the tsunameter automatically transmits data to a surface buoy. The surface buoy makes a satellite connection to Tsunami warning centers that evaluate the threat and issue a tsunami warning. The most important sensing requirement is the detection of very small pressure changes at water depths up to 6000 meters. The change in water depth due to a tsunami in the open ocean is generally less than one centimeter. The resolution capability of Digiquartz Broadband Depth Sensors makes it possible for tsunameter to detect water level changes of less than one millimeter at the deployed depth of 6,000 meters (one part in six million).
Top 10 Features Of Tsunami Warning System :
The tsunami warning systems are one among the needed significant gadgets and technologies that allow people to be cautious and warn before the calamity strikes. Some technically ahead countries have readily fixed big systems for detecting tsunami beforehand. The small tools that are found by engineers and other professionals are also hugely useful for caution and safety. Let us look at the top 10 features and the types of tsunami warning system;
1. DEEP-OCEAN ASSESSMENT AND REPORTING OF TSUNAMI (DART)
The DART follows the procedure of detecting the variance in sea levels beneath the ocean bed of a large waterway. The system produces signals through a fixed buoy and allows the user from a respective area or receiving station to get results from the specific satellite.
2. TIDE GAUGE
The tide gauge is useful when the DART system is comparatively costlier to use for installment. The tide gauge follows the norms of GLOSS (Global Sea Level Operating System), which enables the authorities to take steps readily for an upcoming tsunami event that is detected from the gauge’s pinpointing.
3. SEISMOMETER
The seismometer or seismograph will give signals about the seismic waves of the earth rotation in detecting any calamity that is to occur lately. The seismometers provide data about the motion of the earth by observing a particular weight on a specific geographic location.
4. DIGIQUARTZ PRESSURE RECORDER
The depth sensors to record and warn about the signal forms are the major strength of pressure recorders in detecting a tsunami before the event occurs. The device record the pressure levels of a point continuously and when the pressure exceeds the system gives the warning about an upcoming disaster.
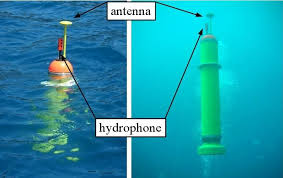
5. HYDROPHONE
A hydrophone is a form of acoustic transducer useful for tsunami detection. The device is electrical and converts the sound waves of a waterbed into electrical radio waves and gives results regarding the level of rising in water level. The electrical plates are exposing through the vibrations present in the wave of water.
6. TSUNAMI ALARM
The tsunami alarm gives sounds of alerts when there are the chances of an earthquake or tsunami is yet to strike the place. The tsunami alarm has the prominent advantage of providing personal warnings in sound forms directly to your smartphone itself.
7. BRINCO
The Brinco is a small and round metallic cylinder that takes only a minimum space of area for installing it. The home device gives owner personalized warning signals to detect earthquakes and tsunami with the help of seismic monitoring systems.
8. OMRON D7S SEISMIC SENSOR
The Omron D75 is the world’s smallest gadget that allows the user to get signals for the tsunami from a particular area. These sensors have the primary advantage of low electricity consumption and high precision in the results given. Packaging downsize is majorly reduced and allows the person to fix this sensor to any device of convenience.
9. SONARDYNE
The Sonardyne uses the regulations and norms of Compactt-6, a subsea transponder. The advantage of sonardyne is that they give complete results of a tsunami even in the most crucial and acoustic conditions. The reliability of these instruments is high. The sonardyne is also useful in the areas of oil and gas companies and industries due to its high predictability and reliance of results.
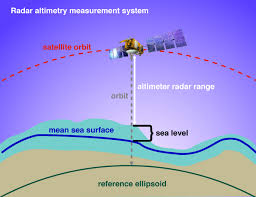
10. SATELLITE ALTIMETRY
The satellite altimetry was found by accident in 2004 during the Indonesian tsunami. The satellite is advantageous by able to detect and measure the whole wave itself on its own. The focus is currently on studying the ocean wave measurements with satellite altimetry.