Wondering what is brain fingerprinting?Well you’ve come to a right place. Let’s first get a brief idea about it!
- Brain fingerprinting is a technology designed to detect concealed information stored in the brain.
- Actually,it’s a lie detection technique which uses electroencephalography (EEG) to determine whether specific information is stored in a subject’s brain.
- Moreover, this technique consists of measuring an electrical brain wave response to specific stimuli such as words, phrases or pictures presented on a computer screen.Interesting, isn’t it?
Process of BrainFingerprinting
Having a basic idea about brain fingerprinting now let’s have a look over it’s working.
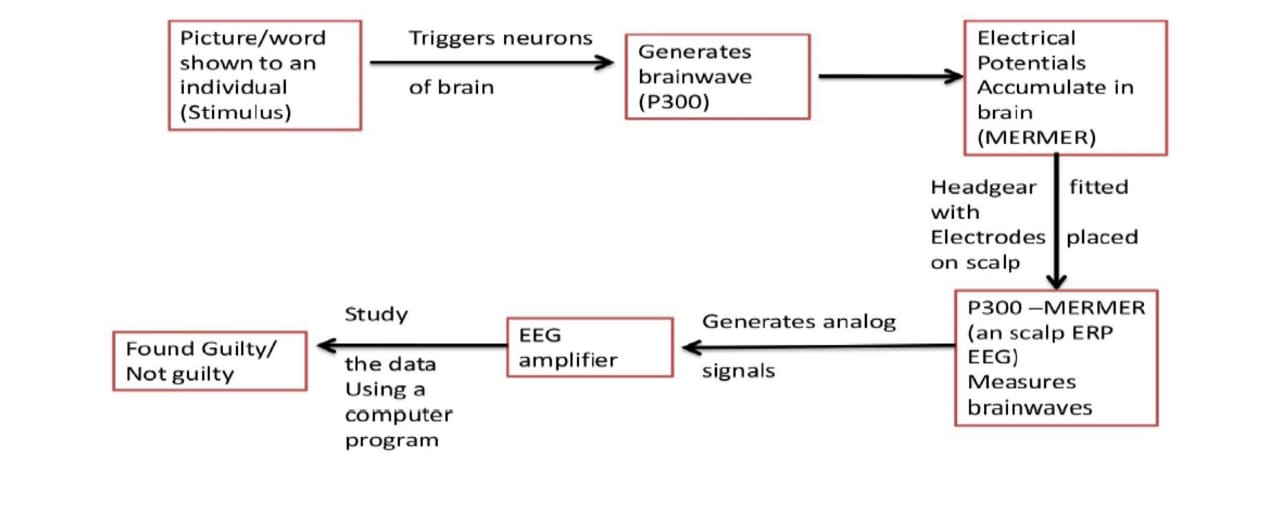
- Brain fingerprintingis accomplished by measuring the subject’s brain response to stimuli in the form of words or pictures presented briefly on a computer screen.
- During a brain fingerprinting test, electroencephalograph (EEG) signals are recorded non-invasively from the scalp
- The test uses electroencephalography (EEG) to study the electrical behaviour of the human brain.
- The suspect is seated in a comfortable chair in a soundproof room with a cap having dozens of electrodes attached to it.
- The other ends of the electrodes are connected to an electroencephalographic (EEG) machine.
- The suspect is then shown visuals or audio clips related to the case to check if there is any triggering of neurons (P300-MERMER) in the suspect’s brain which then generate brainwaves.
- The specific, measurable brain response known as the P300-MERMER is emitted by the brain of a subject who has the details of a crime stored in his brain, but not by a subject lacking this record in his brain. So now we understood it’s working. Now, you may be wondering regarding the first use of brain fingerprint. So, let’s discuss that as well.
The first use of brain fingerprint
In the year 1999, a woodcutter named James Grinder confessed murdering a woman named Julie Helton. Helton died 15 years prior to Grinder’s confession. Shortly afterwards, the man retracted his statements, contradicting himself time and time again.
The police were struggling to device a strong case against Grinder as the pieces of evidence were decades old. Thus, the Sheriff called Dr. Lawrence Farwell who discovered a new way to determinate the guilt or innocence of a suspect by measuring the brain activity.
During this test, short phrases were viewed by Grinder flashed on a computer screen. Some of these phrases were related to the crime that would be known only to the perpetrator.
The computer analysis of the test found that these details of the crime were recorded in his brain as ‘information present’.
The legitimacy of Brain Fingerprinting
- It is a legitimate neuro-psychological method of interrogation.
- However, test results alone cannot be admitted as evidence.
- Moreover, as per an SC judgement in 2010 Selvi versus State of Karnataka caseany information or material discovered during the tests can be made part of the evidence.
LIMITATIONS OF BRAIN FINGERPRINTING
- Brain fingerprinting detects information-processing brain responses that reveal what information is stored in the subject‟s brain. It does not detect how that information got there, be it a witness or a perpetrator.
- Brain fingerprinting is not applicable for general screening.
- Brain fingerprinting detects only information, and not intent.
- Just as all witness testimony depends on the memory of the witness, brain fingerprinting depends on the memory of the subject.
- Brain fingerprinting does not detect lies. It simply detects information. No questions are asked or answered during a brain fingerprinting test.